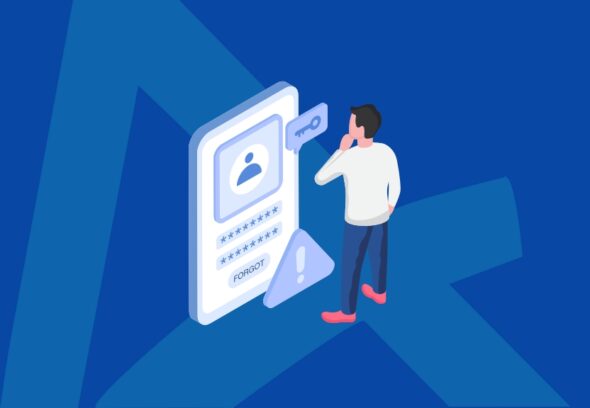
A large number of organizations have not abandoned the traditional approaches to identity management were developed and deployed several years, or even decades, ago. Even though these systems were found useful in the past, they have now become sources of serious security threats that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information.
Organizational identity management systems of the past may not have the same type of security as today’s solutions. They can use old fashioned modes of authentication, may not have adequate encryption standards or may not be compatible with modern security appliances and systems. Consequently, such systems can further be at risk of a number of cyber threats such as data leaks, unauthorized access as well as identity theft.
The information about the threats connected with the usage of legacy identity systems can help organizations to prevent potential risks and protect their digital resources and customers’ data. When these risks are understood, you are able to make the right decision for identity management infrastructure modernization and secure controls adoption.
Security Risk on Business and Consumer
The penalties that result from security breaches arising from weak legacy identity systems are not only painful, but they extend far and wide. That is why a breach of data in companies can lead to direct financial losses, damage to reputation and violation of the law. The actions for compliance check, assembling and reporting a violation, repairing a violation, peculiarly informing the impaired citizens, and perhaps, facing the money penalty or law demands can accumulate rather significant amounts.
In addition, a breach to an identity system brings with it risks that include; unauthorized access to information and data, theft of intellectual property and indeed business disruption. This can erode customer trust and confidence and will have a negative effect on an organization’s profitability and competitive position.
The consequences for the consumers are just as grim as for the company – identity theft and data breaches. People’s delicate data including their financial records, medical histories, passwords and so on, might be accessed by the wrong people and leads to embezzlement, identity thefts and invasion of privacy. The issue with such occurrences is that they cause emotional stress and to sort it out, may take a lot of time.
Evaluating the Risks of Your Legacy Identity Systems
To avoid various issues that are associated with legacy identity systems, it’s important that an organization performs an evaluation of the security posture. This assessment should encompass the following aspects:
- Inventory and Mapping: Do a reconnaissance of all inherited identity systems in your organization and establish their dependency, connectivity and data exchange.
- Vulnerability Analysis: Assess the risks eternal and exploitable in these forms of system like old protocols or nonexistence of encryption or obscure access rights.
- Risk Assessment: Estimate the risks connected with security breaches or incidents in connection with each of the legacy identity systems based on the data sensitivity and business-criticality of the systems.
- Compliance Review: Make sure your existing identity systems are built with compliance with current laws and regulations including GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS in case you operate in the particular sector and region.
- User Experience Evaluation: Review the experience customers have with the legacy identity systems because if the process of authentication is cumbersome or confusing, it will lead to either user workarounds or non-compliance.
By so doing, you are able to establish the security risks that are most imminent and address them before anything else.
Approaches to Managing Security Threats in Old-School Identity Solutions
While a complete overhaul of legacy identity systems may be the ultimate solution, there are several strategies you can implement to mitigate security risks in the interim:
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA enhances security whereby identity authentication requires a user to enter a password followed by a code, or fingerprint. This can help to greatly decrease the threat of a break-in, even if one of the authentication factors is a threat.
- Enhance Encryption and Cryptographic Protocols: Revise your existing encryption algorithms and protocols to modern and best of class standards. This can reduce the susceptibility of specific data in transit and at large thereby reducing possibility of theft.
- Implement Least Privilege Access Controls: Effective correctly control system permissions and access rights and minimize the privilege for the users to only that that is required in their job description. This can reduce the system’s exposure to risks arising from a compromised account or an insider threat.
- Integrate with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools: Incorporating your existing identity systems with your SIEM tools helps consolidate your logs, as well as track user activity, and identify possible security threats or suspicious activities in real time.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Hire security professionals who check and penetration test your old identity systems frequently. It can then assist in revealing risks and holes in the system before the adversary claims them for exploitation.
- Implement Robust Patch Management and Vulnerability Remediation Processes: Make certain that you have solutions for systematically implementing fixes for security and for handling vulnerabilities that have been discovered in the old identity systems, thus minimizing the time that a system remains vulnerable to threats.
However, it should be noted that with these strategies, the risks are reduced only temporarily. Finally, updating your identity management infrastructure should be a goal that is on the top of your list for long term planning and protection.
Modernizing Legacy Identity Systems: Best Practices
Identity management is a process of migrating from the old and often insecure identity systems to new ones, which is not an easy task. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Establish a Cross-Functional Project Team: Get together a group of people who belong to different departments including IT, security, compliance and business segments. This cross functional approach ensures that all stakeholder needs and requirements are meet.
- Define Clear Objectives and Success Criteria: Identity modernization objectives can be defined as specific goals meant to be achieved by your identity modernization project – for instance, you might aim at increasing security, enhancing the experience of users, or enabling new lines of business. Measure the success criteria in such a way that major and minor achievements can be tracked down and correlated with set goals.
- Conduct a Comprehensive Requirements Analysis: Make a detailed assessment of your organization’s existing and future identity management needs, taking into account questions of growth potential, compatibility with current IT systems, and legal requirements.
- Evaluate Modern Identity Management Solutions: Discuss numerous contemporary systems of identification management and the choice between cloud and on-premise. Evaluate their attributes; strengths and functions to provide security to your organization’s infrastructure and conform to its needs.
- Develop a Phased Migration Plan: Develop migrants for each phase for the total solution identity management with an emphasis on the time frame required to complete each step. This should involve the approach that should be adopted in migrating data, approach to be taken when onboarding users and any other problems that may arise.
- Implement Robust Security Controls: When selecting a new solution for identity management, make certain it enforces best security practices including: utilizing multi-factor authentication, high levels of encryption, and even element-based access restrictions. Expand it as part of a security solution that combines hardware, software, and user practices to form a multi-layered security system.
- Provide Comprehensive User Training and Support: Changed awareness users about the new identity management system and focus on security measures and usage. Provide follow up assistance and tools needed to ensure a favorable transition.
- Continuously Monitor and Improve: Ensure that the new identity management contains check points for monitoring, auditing and making subsequent improvements. One of the most important policies is to ensure security policies, procedures, and controls are reviewed and updated periodically to reflect the best security practices.
The above best practices should be adopted to effectively modernize identity management infrastructure to overcome legacy systems security threat while at the same time embrace new opportunities in business and improved user experiences.
Conclusion
Old identity systems are a huge security threat that can have disastrous effects on industries and customers. These are why it is important for organizations to appreciate these risks and spur to actions meant at reducing the risks commonly associated with leaking of sensitive data, non-compliance and damaging of organization’s image.
As effective as it may be to apply short-term workarounds to bounce back from an ID management crisis, the way forward is to upgrade your identity management systems. To optimize identity management today and prepare for tomorrow, ensure you adopt fresh, safe solutions and align with the current best practices, while shedding the legacy issues that hamper your organization’s innovation and security.
Sign up for your free trial now and discover the capabilities of a current and safe ID management system. Preserve your organization’s digital resources and make sure your customer’s data is protected with our advanced technology.