The work-from-home world introduces new IT security challenges. To keep up with these challenges, it is critical to understand the challenge first.
What’s at Stake For Security In A Remote Work World
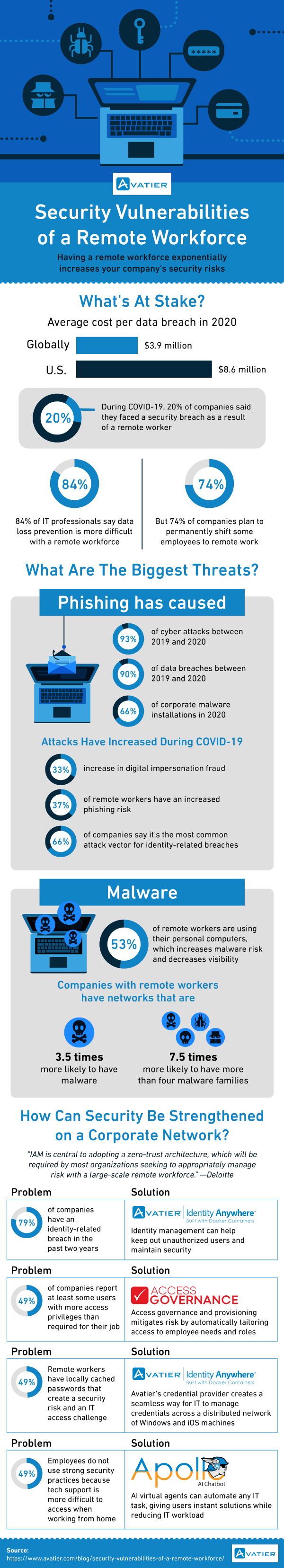
The latest industry research shows that data breaches are now costing companies millions of dollars. In the United States, each data breach now costs about $8.6 million. On a global level, the cost is $3.9 million per data breach. Unfortunately, the COVID-19 pandemic has made IT security even worse.
Twenty percent of companies say they have faced a security breach due to a remote worker. That’s a problem because remote work arrangements are likely here to stay in some form for a long time to come. Therefore, we need to understand the specific nature of security threats linked to large-scale remote work.
Share this Image on Your Site!
Simply copy and paste the code below and you can share this infographic on your site:
<a href="https://blog.avatier.com/security-vulnerabilities-of-a-remote-workforce/"><img alt="Security Vulnerabilities of a Remote Workforce" src="https://blog.avatier.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/security-vulnerabilities-of-a-remote-workforce-infographic.png" width="600px" height="3313px" /></a><br><a href="https://blog.avatier.com/security-vulnerabilities-of-a-remote-workforce/">Security Vulnerabilities of a Remote Workforce</a> Created By: <a href="https://www.avatier.com/"> Avatier</a>
These Are the Biggest Threats Today
In IT security, there are new threats discovered every day. With so many threats on the horizon, it can be challenging to know where to focus. Fortunately, you can achieve a lot by focusing on two types of threats: phishing and malware. Applying training and software to mitigate these threats is vital to keeping your data safe.
Phishing has caused more than 93% of cyber attacks between 2019 to 2020. Even worse, phishing is the root cause of 90% of data breaches in 2019-2020. Phishing has been around as a threat for a long time. The threat is getting worse in 2020 due to the global pandemic. The latest industry research found that:
● Digital impersonation fraud has increased by 33%. This type of fraud means that an attacker could send a faked email from an executive requesting a change (i.e., “Dear IT, please provide access to the following user.”). Such threats are more challenging to resist because these threats often impersonate multiple details of the impersonated person.
● Remote workers have a 37% higher chance of phishing risk compared to non-remote workers. This trend is likely because remote workers have minimal non-digital communication options. Since nearly all workplace communication goes through digital channels, there is a greater risk of exposure.
● Two-thirds of companies say that phishing is the most common attack vector for identity-related IT security breaches. Improving the quality of identity and access management systems and controls is even more critical.
Malware threats are also evolving to become more significant in a remote security world. A key reason for increasing malware lies in employee behavior. More than half of remote employees use their personal computers for work. As a result, company IT has limited ability to ensure that remote workers are correctly using security software.
Solving The Remote Worker Security Crisis
There are multiple ways to address the reality of large-scale remote worker security. Let’s assume that a significant share of your workforce wishes to work remotely for the foreseeable future. In that situation, IT leaders need practice options. Consider the following solutions to make IT security effective in a remote work
1. Prevent Identity-related Security Breaches
Ultimately, preventing identity-related cybersecurity breaches requires a full identity and access management program. For example, you need to provide password management training to employees so they know how to create robust passwords. IT needs the right tools like Avatier Identity Anywhere to systematically monitor identity in the organization.
2. Prevent Security Problems Related To Access Privileges
An account breach of a single user with extensive access privileges can do a lot of damage to your organization. That’s why managing access privileges is a critical security practice. However, it is not realistic to expect IT staff to review security privileges for every user manually. Instead, you need to leverage a specialized IT security software solution like Compliance Auditor.
Tip: When employees leave their current job for a different role in the company or leave the company, their access privileges need to be updated quickly. To systematize this practice, engage with human resources to determine when employees change or leave the organization. For more guidance on this topic, check out our article: Reduce Employee Fraud Risk: 5 Ways to Improve Offboarding.
3. Implement Better Password Security for a Remote Workforce
With a remote workforce, the right tools are needed to reset locally cached passwords. The user’s computer may keep a critical corporate password stored locally, which creates a security risk and an IT challenge. You can solve this risk by using Identity Anywhere to secure credentials across different computing environments, including Windows and iOS.
4. Add Self-service Password Tools
Automated support is important for a remote workforce. In a conventional office, employees can call IT or visit a help desk to get password help. In a remote work environment, calling the help desk may take more time. As a result, employees may feel a need to use less secure habits (e.g., writing down passwords on scraps of paper). A better solution is to use a self-serve password reset tool like Enterprise Password Management and automated virtual agents like Apollo.
5. Use VPN Security To Reduce Attacks
A virtual private network (VPN) is a vital tool to improve your security. On its own, it will not prevent all attacks. Nonetheless, it is a powerful tool that needs to be in place to support remote employee security. Find out more about the benefits of VPN technology in our article: What You Need To Know About VPN Security.
Tip: Make sure your employees know how to turn on their VPN security. Since using a VPN can impact internet speeds, some employees may be tempted to skip using a VPN. It is important to reinforce the value of using a VPN to maintain security.
6. Test Your IT Security Controls Regularly
IT security threats keep changing every month. You can find out if your practices have a gap by getting attacked, or you can protectively detect that gap yourself. To minimize the chance of an expensive data breach, use an IT security testing program that considers remote worker security concerns.
For example, you might decide to give employees a knowledge test quarterly to see if they are aware of phishing risks. Some companies also send simulated phishing messages to their employees to evaluate whether employees are equipped to detect and respond to these such threats. Finally, check whether your controls are working. For example, are managers reviewing user access privileges in their department regularly? Such access reviews can go a long way toward closing security vulnerabilities before they become a problem.
7. Review Remote Employee Physical Security Practices
The security systems and practices outlined above cover the fundamentals of adequate IT security for remote work. However, it is also worth taking another look at physical security practices. For example, do you have a process to prevent employees from printing sensitive documents at home? If not, applying controls to such printing is worth taking a closer look at since it may lead to unauthorized data disclosure.




